Have you felt like this recently?
Have you every suddenly thought "Oh! I can't see well!"
It's important that you don't just ignore it by saying "I must be tired" or "It's my age". In some cases, the cause could be an eye disease. If the progression is gradual, people may not notice if they don't pay attention.
At times like this, please take another look at the health of your eyes.
Below, we introduce the structure of the eye, and some symptoms that might signify eye disease.
Possible symptoms of eye disease
The following are examples of possible symptoms of eye disease
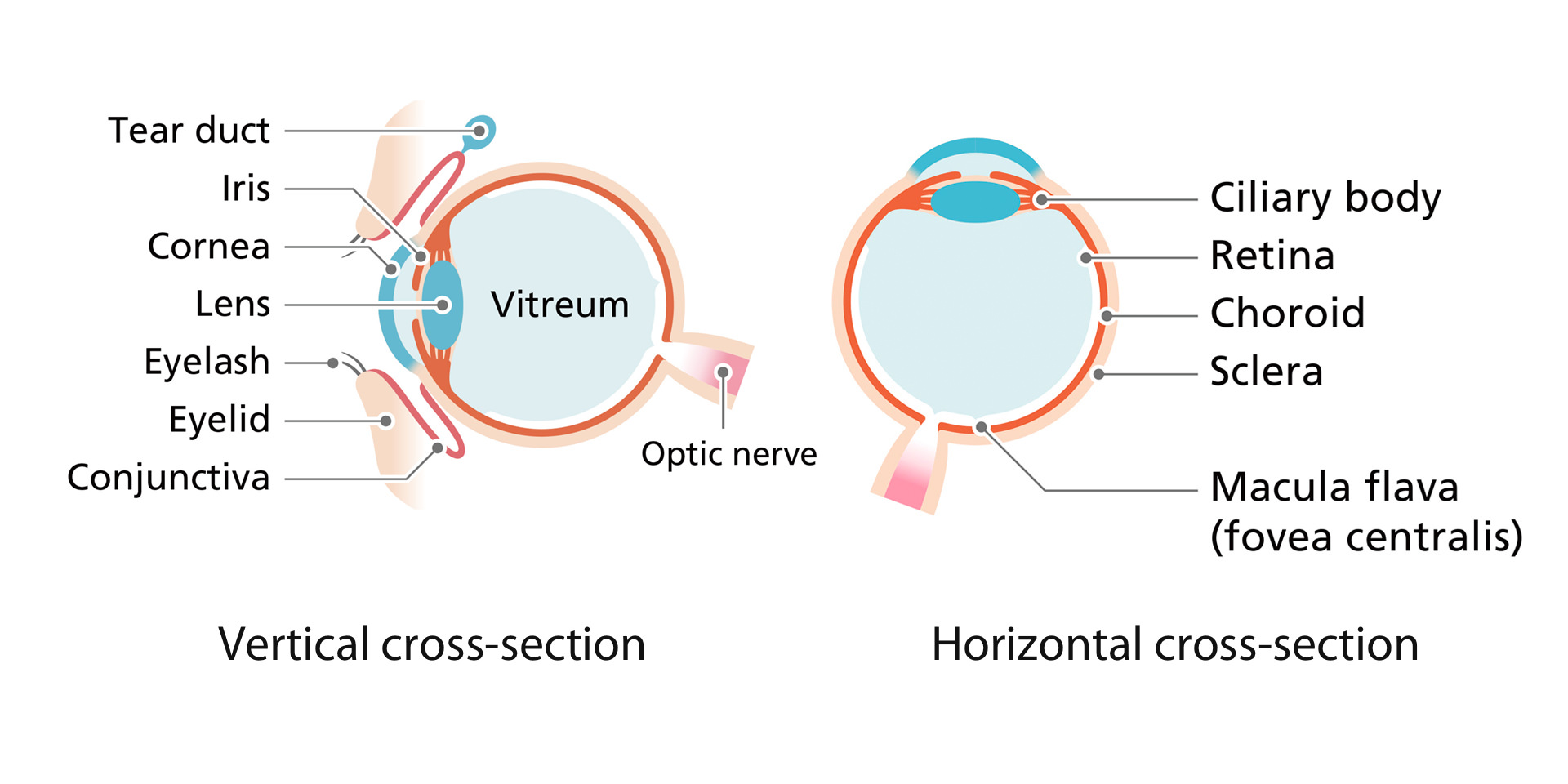
The structure of the eye
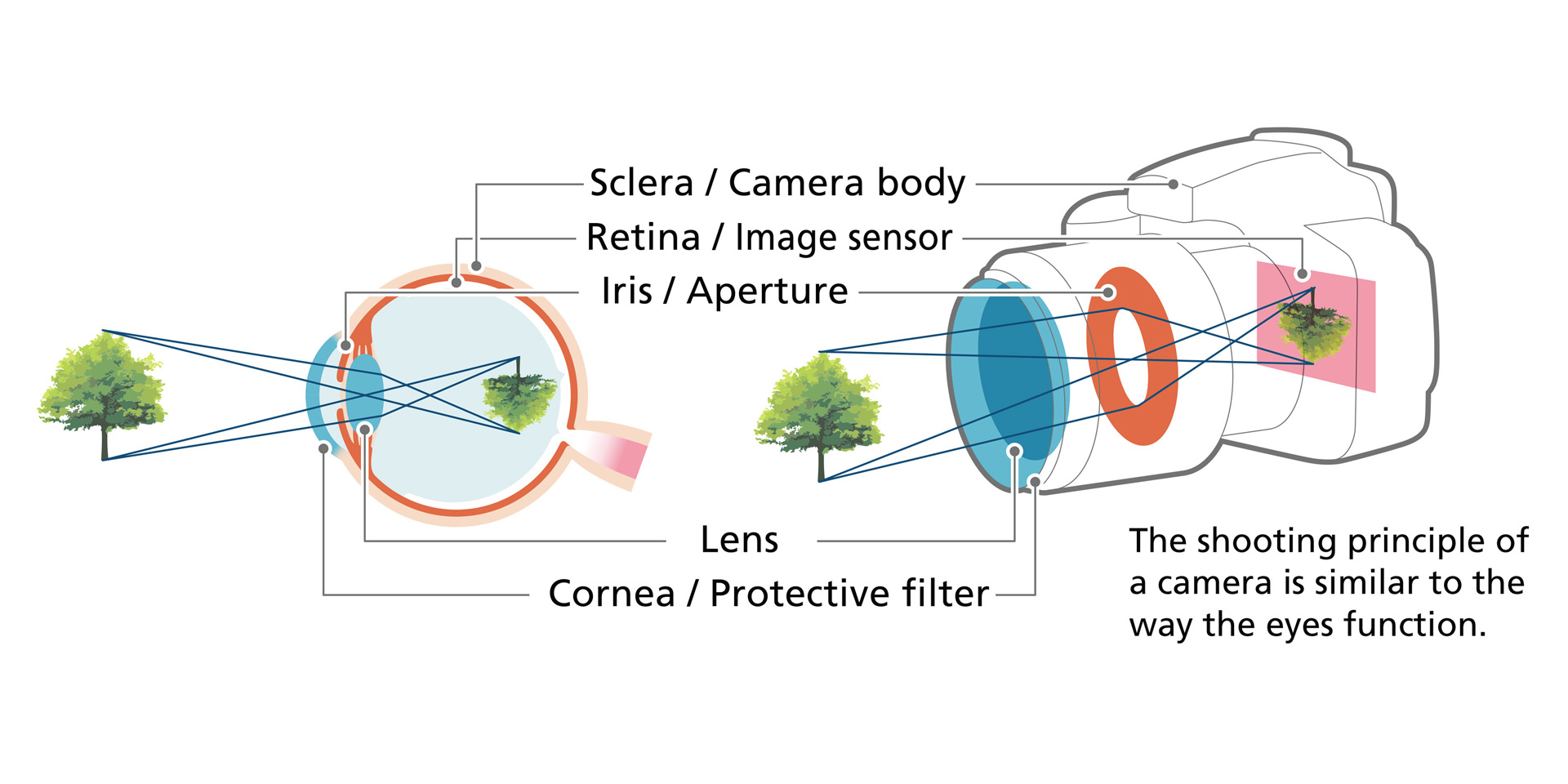
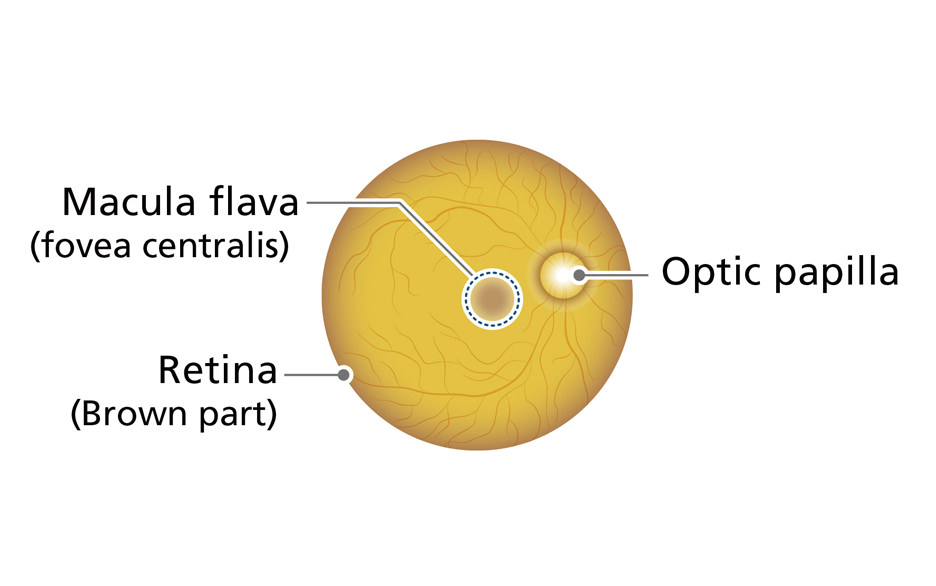
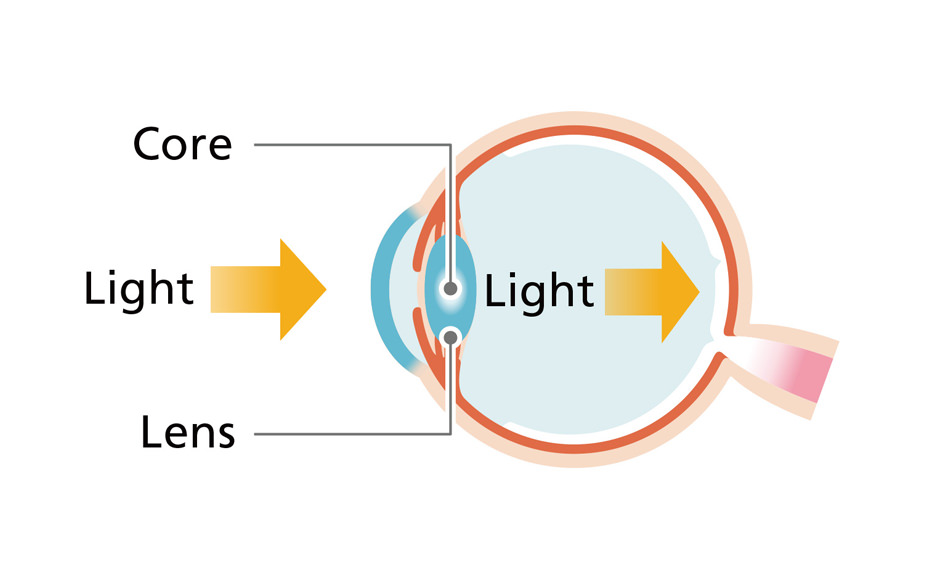
Your eyes have the role of seeing things. Light entering through the pupil passes through the lens, and is formed into images by the retina, which is at the back of the eye and is criss-crossed by capillary blood vessels and the optic nerve. That image information is transmitted to the brain, where it can be recognized as shapes, colors, and movements. The eye is a very complex and intricate sensory organ. Let's stay aware of changes in how we see things, which bother us a little day by day. That change could be a symptom of eye disease. If a symptom that you notice continues, we advise you to have your eyes tested. Please listen to the "voice" of your vitally important eyes.
Possible symptoms of eye disease 1:
My eyes are hazy
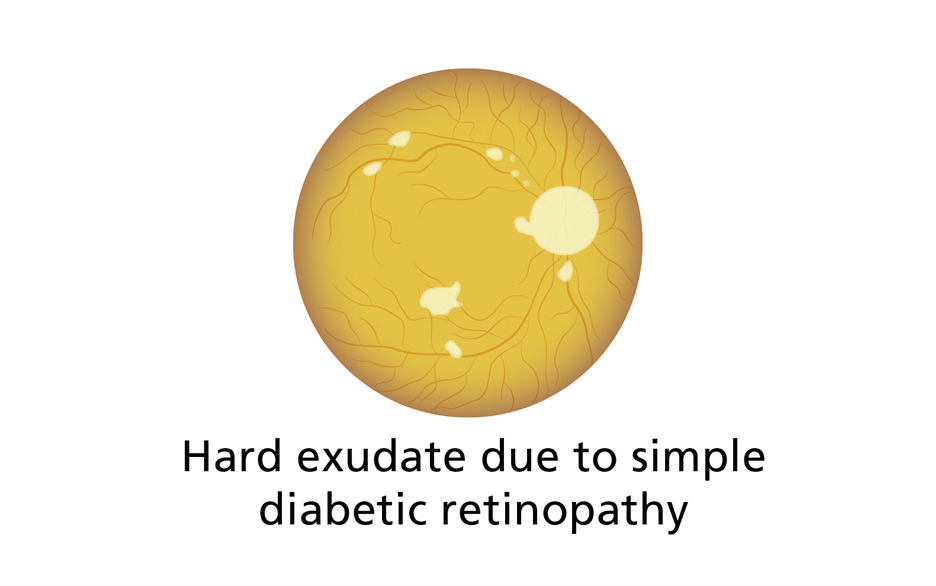
Could it be diabetic retinopathy?

What kind of disease is diabetic retinopathy?
In this disease, the retinal tissue at the back of the eyeball is harmed by diabetes, causing loss of eyesight. The main cause is bleeding from capillary blood vessels that are weakened by diabetes. It is said to be one of the big three complications of diabetes, alongside diabetic nephropathy and diabetic neuropathy.
What are the symptoms?
In the early stage, there are no obvious symptoms that you can feel. With progression into the middle stage, noticeable symptoms such as haziness in the field of view start to emerge. Disease progression can be suppressed with early treatment. Follow your attending doctor's instructions and don't miss your regular eye
Possible symptoms of eye disease 2:
It's blurry and hard to see
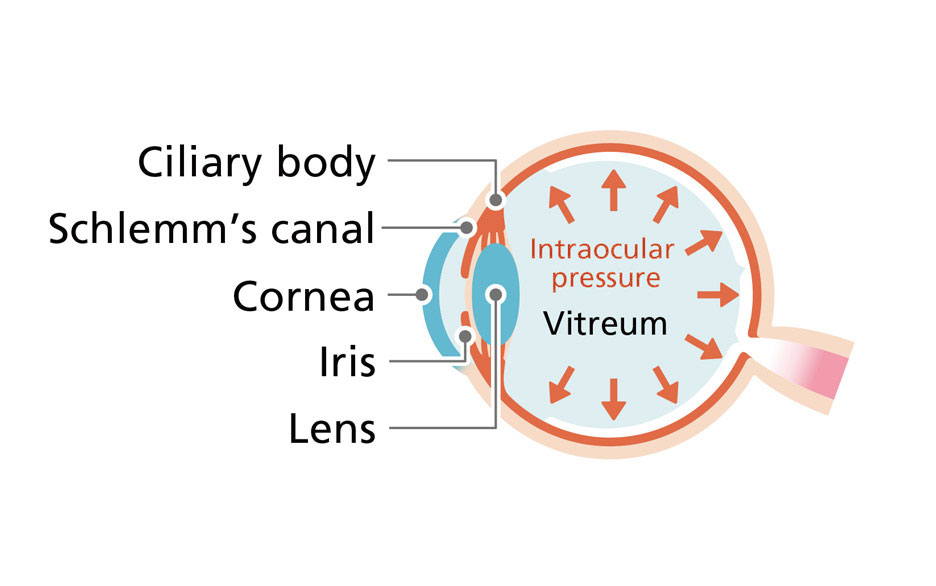
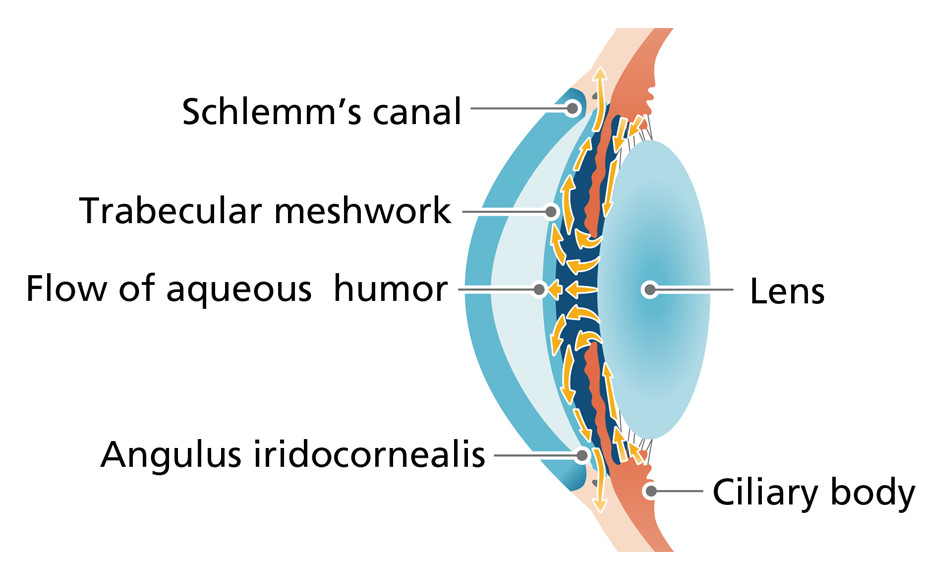
Could it be glaucoma?

What kind of disease is glaucoma?
A fluid called aqueous humor circulates inside the eyeball. It is secreted by the ciliary bodies and acts in place of blood to move the nutrition the eye needs. Then it is expelled at the Schlemm's canal. The aqueous humor circulates under a constant pressure, which is called "intraocular pressure". In glaucoma, the balance between secretion and expulsion of aqueous humor breaks down, and intraocular pressure rises, placing pressure on the optic nerve.
What are the symptoms?
For example, loss of part of the field of view, with things looking blurry. It is the leading cause of loss of vision in Japan, so we advise an early eye examination.
Possible symptoms of eye disease 3:
The middle of the pupil is white
Could it be cataracts?

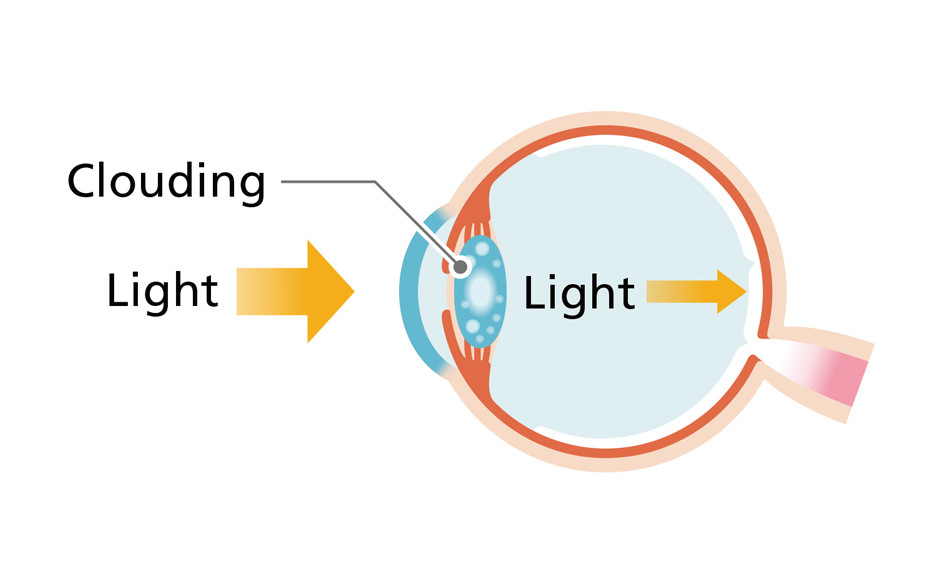
What kind of disease is cataracts?
It's a disease that turns the lens of the eye white and cloudy. The cause is said to be degradation of protein, mainly due to aging. The lens, which should be clear, turns white and cloudy, so that the light the eye has gathered doesn't reach the back of the eye well.
What are the symptoms?
The clouding of the lens may make the black of the pupil look white, cause hazy vision, reduce visual acuity, or produce other symptoms. In the early stages, progression can be suppressed by treatment with eye medicine etc., but once further progression starts to impede life activities, surgery is required. Follow your attending doctor's instructions and don't miss your regular eye checkups.
The ultra-widefield retinal imaging device is busy in eye testing facilities.
Pathological changes accompanying eyeground diseases occur not just in the central area of the ocular fundus, but also in its periphery. The ultra-widefield retinal imaging device can capture wider images of the ocular fundus, out to its periphery with a 200° field of view, so it assists the early discovery of pathological changes in the ocular fundus.
If you are bothered by any other eye symptoms and they do not get better, get an eye checkup quickly.


