Accurate measurement cell density within hPSC colony for determining optimal passage timing
Point
It is important to assess the loose or tight packing density of hPSC (including both hiPSC and hESC) colonies in order to understand cell condition and determine the timing of passaging.
Overview
While there are some variations that are dependent on the hPSC culture conditions, cells are generally relatively big immediately following seeding, and form colonies that are loosely adhered with each other. As culturing proceeds, colonies change shape and their cells adhere to each other more tightly.
Undifferentiated hPSCs gather and form colonies regardless of whether clump passaging or single cell passaging is applied. As culturing continues, colonies become what is referred to as a "mature colony," where cell morphology is homogenous in the mature part of the colony, cell density is high inside the colony, and the boundaries between cells in the colony are unclear.
Current
Issue-1
hPS cell characteristics are unstable and susceptible to changes caused by the culture environment.
Inappropriate culture conditions lead to instability in cell characteristics, resulting in phenomena where colonies fail to mature, or grow to a reduced size.
Issue-2
Lack of (skilled) resources and experience
Assessment of colony loosely/tightly packing is important for understanding cell health and informing the timing of passaging. Visual assessment requires years of operator experience, resulting in a shortage of qualified personnel able to handle the task.
Solution
hPSC colony loosely/tightly packing is determined using non-invasive phase contrast imaging and image analysis.The loosely/tightly packing of hPS cells in each colony is assessed using phase contrast imaging and analysis. Time-lapse image acquisition enables quantification of the ratio of loosely packed colonies to tightly packed colonies.
Using the BioStudio-T*, a cell observation system that can be installed inside an incubator, phase contrast images of cells can be captured over an extended period without perturbing the culture environment.
*This product has been discontinued. If you have any questions about cell cultures, assays, or products, please contact us using the contact form.Cell image analysis software Cell Analysis Module
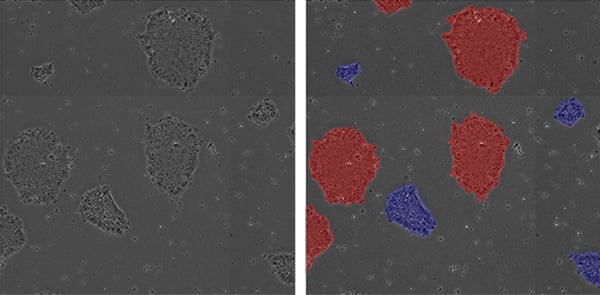
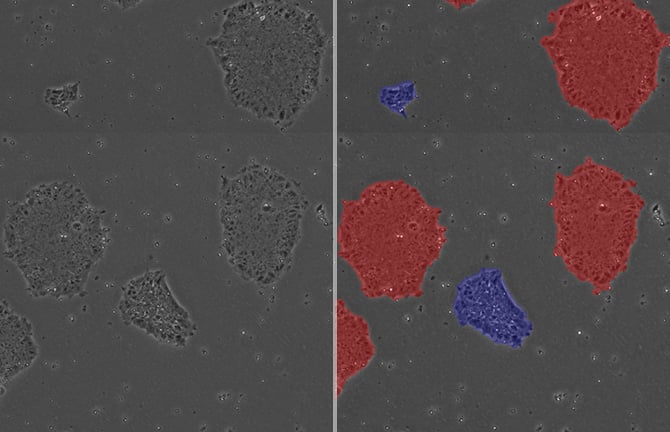
Non-invasive measurement of colony loosely/tightly packing by phase contrast imaging and image analysis. Blue masks represent loosely packed colonies, and red masks represent tightly packed colonies.
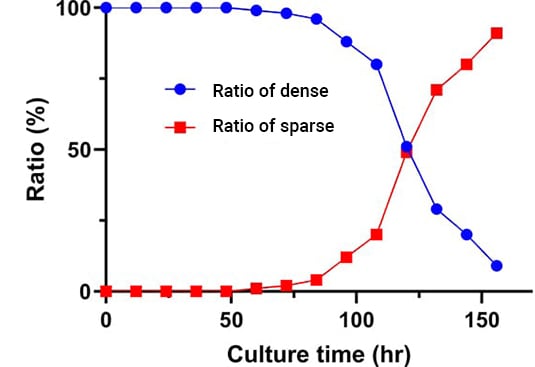
Changes in the ratio of tightly packed colonies to loosely packed colonies over time can be plotted as above.
Utilization scene
As an evaluation index for establishing cell culture processes
- Assessment of the effects of culture conditions (media composition, passaging methods, variability in procedures among operators, etc.)
- Determination of passage timing.
Reference
Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4 (7):720-30
Nikon will contribute to solving your cell culture issues with its image analysis
techniques and know-how on cell quality evaluation.
Click hereInquiry Form