User interviews《Cyfuse Biomedical K.K》Enhancing operating efficiency in the CPC (Cell Processing Center) realizes a more comfortable environment for both people and cells.
“Time-lapse imaging was employed to evaluate indicators for 3D tissue/organ manufacturing, linking the process to results.”
Cyfuse Biomedical K.K
Main Business fields
Development, production, and sales of regenerative medicine products
Interviewees
Research and Development Department Clinical Development Group Clinical Facility LeaderEmi Oshima
Research and Development Department Basic Research and Development GroupAyana Sonoda
Adopted equipment/systems

‘Create Hope from Cells’ — Cyfuse Biomedical K.K.(hereinafter Cyfuse) strives to provide new treatment options by using its 3D Bio Printing technology platform. Fusing biology and engineering with sophistication, Cyfuse has developed a Bio 3D Printer equipped with its revolutionary technology. They have succeeded in creating 3D tissues/organs, such as blood vessels, consisting solely of cells. This is a significant contribution to the rapidly evolving field of regenerative medicine. Thanks to its high-resolution and time-lapse imaging capabilities, Nikon’s BioStudio-T is helping identify efficient indicators for use in 3D tissue/organ manufacturing, which has become the basis for the industrialization of regenerative medicine. In this interview we spoke to Emi Oshima and Ayana Sonoda, who are actually working with BioStudio-T about its usability and effectiveness.
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
Contents
ShowCyfuse innovation

Creating 3D tissues/organs using only cells.
Cyfuse is working towards the industrialization of regenerative medicine. Please tell us about what kind of treatments you are developing.
“By using a Bio 3D Printer equipped with original technologies, we are aiming to develop 3D tissue/organ products that may become a new treatment method that restores the original function of the body through creating such products then transplanting them into patients. What makes our products differ greatly from conventional regenerative medicine products is that they are produced from cells only, without using any artificial materials.”
What are the benefits of Cyfuse’s 3D tissue/organ products?
“Until now, there have been hybrid composites of cultured cells with scaffolds made of chemicals or animal-derived biomaterials. However, there are various concerns about using animal-derived substances, such as the fact that they can cause inflammation due to allergic responses and infections due to virus contamination after transplantation.
On the other hand, our 3D tissue/organ products made only from cells generally have a low risk of infection. Also, since they have the same thickness and elasticity as the original tissue, they can be sewn with thread. Therefore, they can be utilized in actual transplant surgeries. We are currently conducting several clinical trials with our collaborators.”
What kind of processes are required to create such 3D tissue/organ products?
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
We are working on developing regenerative medicine products using scaffold-free cell- based tissues/organs for cartilage damage, angiopathy, nerve damage, and other disorders. These studies are currently undergoing clinical trials.”
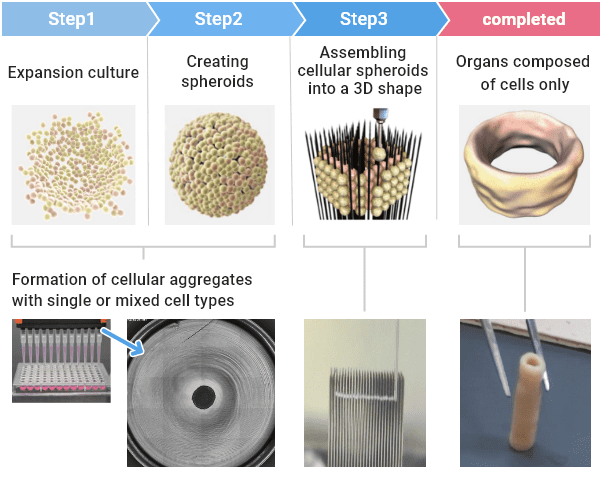
Example of cell-based artificial blood vessel made with a Bio 3D printer.
Are actual patients’ own cells used to create these materials?
“Yes, we’re using the patients’ own cells. Although cell types differ depending on the tissue being produced, we are utilizing types such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and fibroblasts. From a technical perspective, since we can use human iPS cells for material, we are also developing products utilizing other people’s cells or iPS cells as part of our next-generation pipeline.”
Are many cells required to make tissues or organs?
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
Challenges prior to introduction

Media exchange work at the CPC. It is also possible to display cell observation images on the wall monitor of the safety cabinet.
Easier conditions for both workers and cells are provided thanks to enhanced operating efficiency within the CPC.
What is the most challenging aspect of cell culture and production?
“By placing BioStudio-T inside the incubator, we are able to monitor the condition of cultured cells from outside the CPC, and therefore we only need to enter when it is essential. This allows us to create a work environment that is easier on both the staff and the cells.”
Effects of introduction
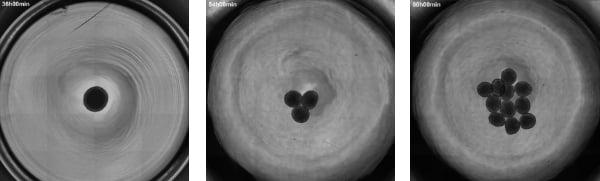
Appearance of a spheroid culture captured with the BioStudio-T time-lapse imaging system. Imaging conditions: phase contrast observation/4x objective lens/tiled image capture of one well. (Image courtesy: Cyfuse Biomedical K.K.)
Identifying indicators through time-lapse imaging that link the cell growth process with results.
How do you feel about using BioStudio-T in the laboratory and the CPC?
“It’s very helpful because we can observe cells via a monitor while culturing them in culture vessels and can also capture time-lapse images.”
I understand that the development of the production process first takes place in the laboratory. In what specific ways is BioStudio-T useful when collecting basic data for the standardization of the culture process?
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
So, we are utilizing BioStudio-T to follow the process of cell aggregation through time-lapse imaging to investigate the differences in the time required for aggregation and the shape, depending on the cell types and the culture conditions. Because images are captured automatically, workers are not required to stay in the CPC, and the burdens are greatly reduced. By collecting large amounts of data in the lab, the conditions for creating spheroids
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.
To industrialize the production of cells that can be applied to clinical practice, it is essential to discover the best growth conditions for each cell type, and BioStudio-T ’s time-lapse imaging function is helpful for this. Is my understanding correct?
“Yes. But not only that, it’s also because it can capture tiled images, the entire culture vessel can be observed, and differences are obvious when comparing the time-lapse images. It’s extremely helpful in determining culture conditions.
Quality control also seems to be a big challenge when it comes to cell production.
“That’s right. The most important thing in the production of tissues and organs that can be used in clinical application is that the hundreds of millions of cells that constitute them need to be of high quality and uniformity. To achieve this, during the final process, we need to observe the state of cells at a given location periodically and quantify characteristics such as cell shape and movement at each stage of the culture process – relating that data to the resulting culture characteristics.
Previously, someone had to be present in the experimental facility for routine observations, and there are some cases where researchers were unable to leave the microscope for over 20 hours.”
When producing cells in the CPC, will BioStudio-T also be utilized to provide indicators during stages such as the quality control of intermediate products?
“Yes, that’s so. When culturing cells, we check their shape and growth, and even that they are not contaminated by bacteria. Currently, these observations are performed by human eyes, so maintaining the training of these workers at the level required is a huge challenge. I think that if image analysis tools such as NIS-Elementsare introduced in the future, maintaining quality will be further simplified.”
- changeovers
- Switching between processes. While using autologous cells, this means switching a process from one patient to a process for a different patient.
Appreciation for the sales system that provided the ideal device solutions for achieving their objectives.
I understand that you are also using a Nikon microscope to inspect the needles used by the Bio 3D Printer.

‘Kenzan’ designed in various shapes. The needles are superfine, with a single needle having a 0.07 mm diameter.
Future expectations

Aiming to produce cells like a food production line.
Could you tell us about your company’s next products and the production ideas you have in mind after obtaining approval for clinical manufacture at this CPC?
“Eventually, we would like to expand the processes that can be completed by machines and add more functions, so that manufacturing can proceed with as little human intervention as possible. However, in reality, there are still many challenges, and steadily dealing with the issues right before us is the highest priority. For the future, we dream about how great it would be to be able to produce tissues and organs like a food production line.”
“In the future, we should first and foremost strive to reliably provide organs produced through our technology to patients. We also hope that we can engage in development that allows us to produce all of the organs within the human body, and then provide the necessary organs required for each different medical department. With the help of our partner companies and the medical personnel at clinical sites, we would like to develop as many regenerative medicine products as possible so that they will be one of the new treatment options.”
Nikon would like to continue to support you in the future as much as possible. Thank you.
*All information is current as of the time of the interviews.Products used currently
Stereoscopic microscopeSMZ745T
Stereoscopic microscopeSMZ745T
In addition to the best-in-class 7.5x zoom and 115mm working distance, this trinocular tube model meets monitoring observation/shooting needs.

Inverted microscopeECLIPSE Ts2
Inverted microscopeECLIPSE Ts2
A simple, compact microscope that fits in any lab. Live samples such as cultured cells can be observed easily and quickly.
Related cases
Nikon will contribute to solving your cell culture issues with its image analysis
techniques and know-how on cell quality evaluation.
Click hereInquiry Form
- spheroids
- Cellular aggregates from various cell types, such as 3D tissues, embryoid bodies, tumor tissue and so on.



