January 31, 2023

(Configured with AX confocal microscope and ECLIPSE Ti2-E inverted research microscope)
TOKYO - Nikon Corporation (Nikon), announced that the NSPARC super-resolution unit, which enables high-resolution deep imaging of living cells and tissues, will be released at the beginning of February 2023. This product will be used in combination with AX or AX R confocal microscopes (released in 2021)※1.
Nikon will continuously add new products to the AX series, consisting of the AX, AX R and the NSPARC to support the research of biological phenomena, and will flexibly respond to customer needs by expanding its product range.
- ※1 Compatible microscopes: ECLIPSE Ti2-E inverted research microscope and ECLIPSE Ni-E motorized upright research microscope
Release Overview
| Product Name | N-SPARC super-resolution unit |
|---|---|
| Release Date | Beginning of February 2023 |
Development Background
In recent years, in research fields such as drug development, brain science, and immunology, there has been an increase in the demand for observation of living cells, living tissues, organs-on-a-chip※2, etc.using microscopes, and to analyze their minute structures, immediate reactions, and changes.
To address these needs, since 2010 Nikon has provided super-resolution microscopes that supersede the limits of resolution of conventional optical microscopes, and contributed to various studies where high-resolution imaging is required. In addition, last year Nikon released the AX and AX R confocal microscopes, which can acquire clear 3D images over a large field of view by scanning a sample with a laser.
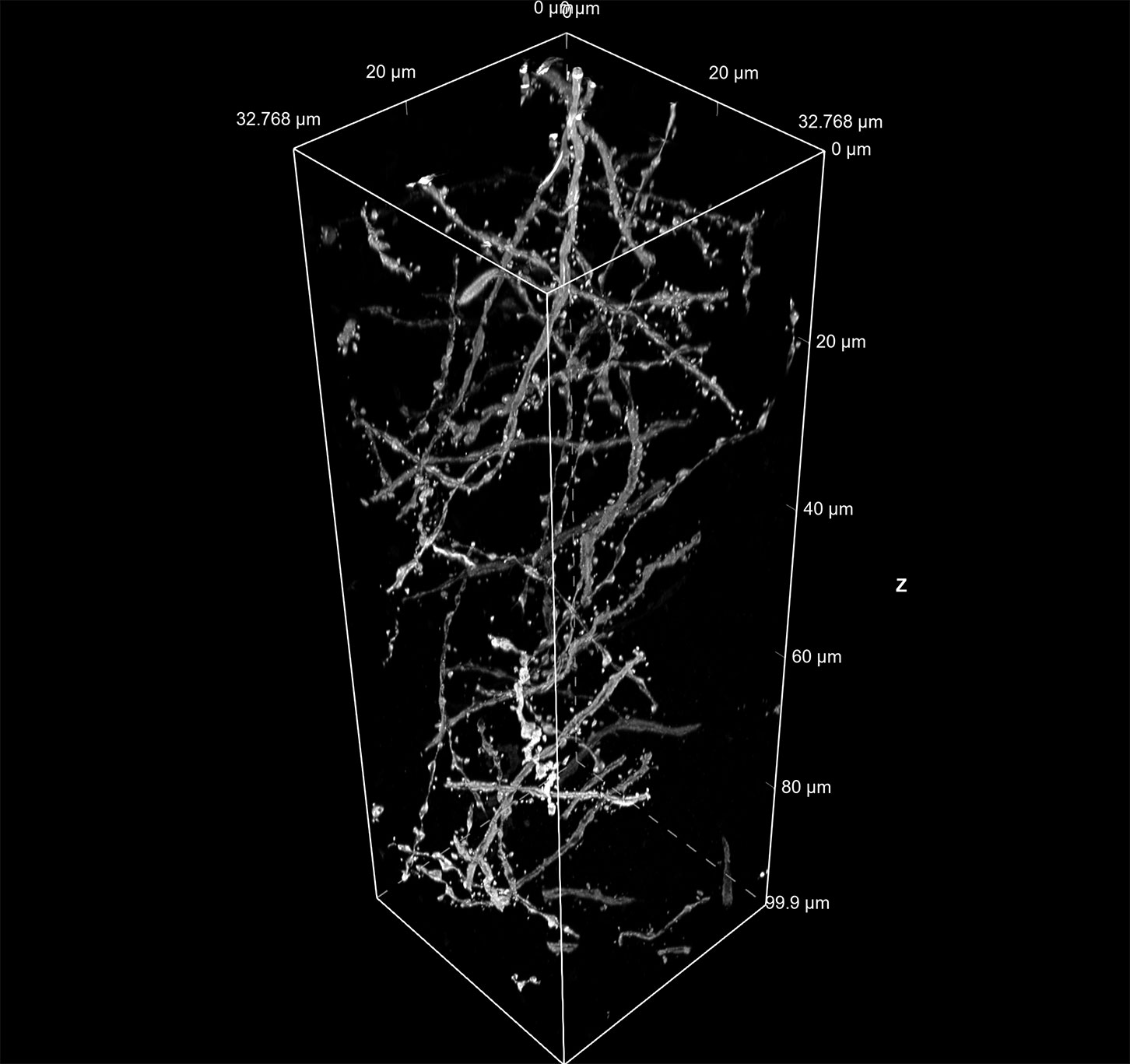
Now, Nikon has developed the NSPARC super-resolution unit, which can capture areas three times or more※3 deeper than the existing N-SIM S super-resolution microscope, and obtain high-contrast 3D images when combined with the AX or AX R. In addition, it is capable of integrating the acquisition and analysis of microscope images and data management when used in combination with the NIS-Elements C imaging software.
The use of this product is expected to contribute to the clarification of the action mechanisms*4 of drug candidate compounds, as well as the disease mechanisms of cranial nerves diseases and cancers, further expanding the possibilities of research.
- ※2 Organ-derived cells cultivated in a minute flow path on a chip simulating an in vivo organ,
which can efficiently evaluate the effectiveness and safety of a drug candidate compound with a high degree of accuracy. - ※3 While the existing N-SIM S super-resolution microscope is capable of deep observation up to 30μm,
the combination of the AX/AX R confocal microscope and NSPARC super-resolution unit is capable of deep observation to 100μm and more. - ※4 Mechanism required for a drug to exhibit an effect
Main Features
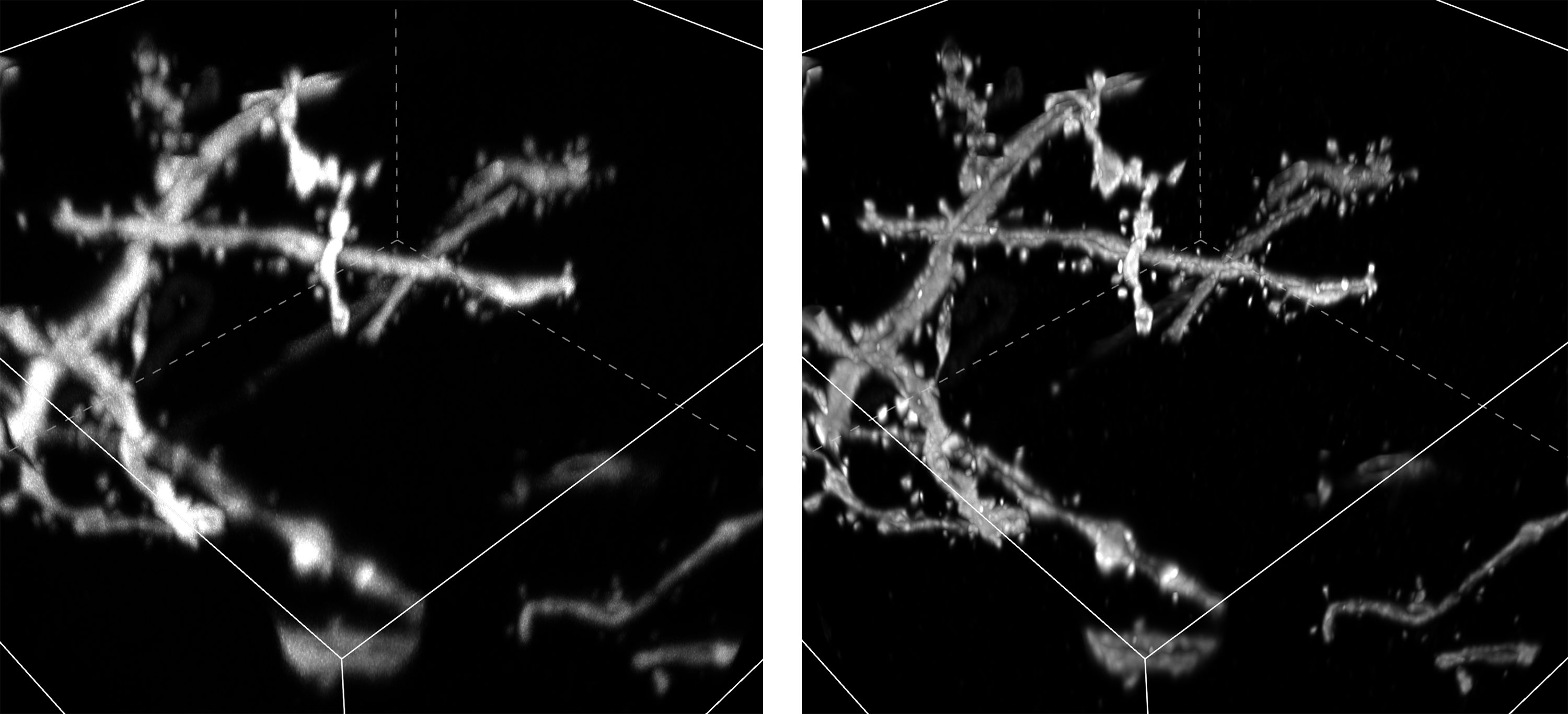
1. Deep imaging down to more than three times that of existing products
NSPARC makes it possible to capture areas three or more times deeper than the existing N-SIM S super-resolution microscope. This enables high-resolution and high-precision morphological analysis of thick samples such as cranial nerves, organoids, and organs-on-a-chip.
Courtesy of: Lin Daniel, PhD., SunJin Lab Co.
2. High contrast 3D imaging
25 single-pixel photon counters located in the photodetector improve sensitivity by 1.3 times※5 to acquire abundant information for each scanning point, which can then be used for image processing. This makes it possible to acquire high-contrast 3D images, even in deep areas where noise is likely to occur, enabling imaging of the fine structures of a sample.
- ※5 Compared to AX and AX R confocal microscopes
3. Alleviation of cell damage that enables high-resolution, stable live-cell assays
By combining NSPARC, which is capable of high-sensitivity detection, and an AX R equipped with a resonant scanner capable of high-speed imaging, detailed sample information can be acquired even during high-speed scanning, enabling high-resolution imaging. High-resolution and stable live-cell assays with less photobleaching and less phototoxicity are made possible by reducing the laser irradiation time and reducing damage to cells.
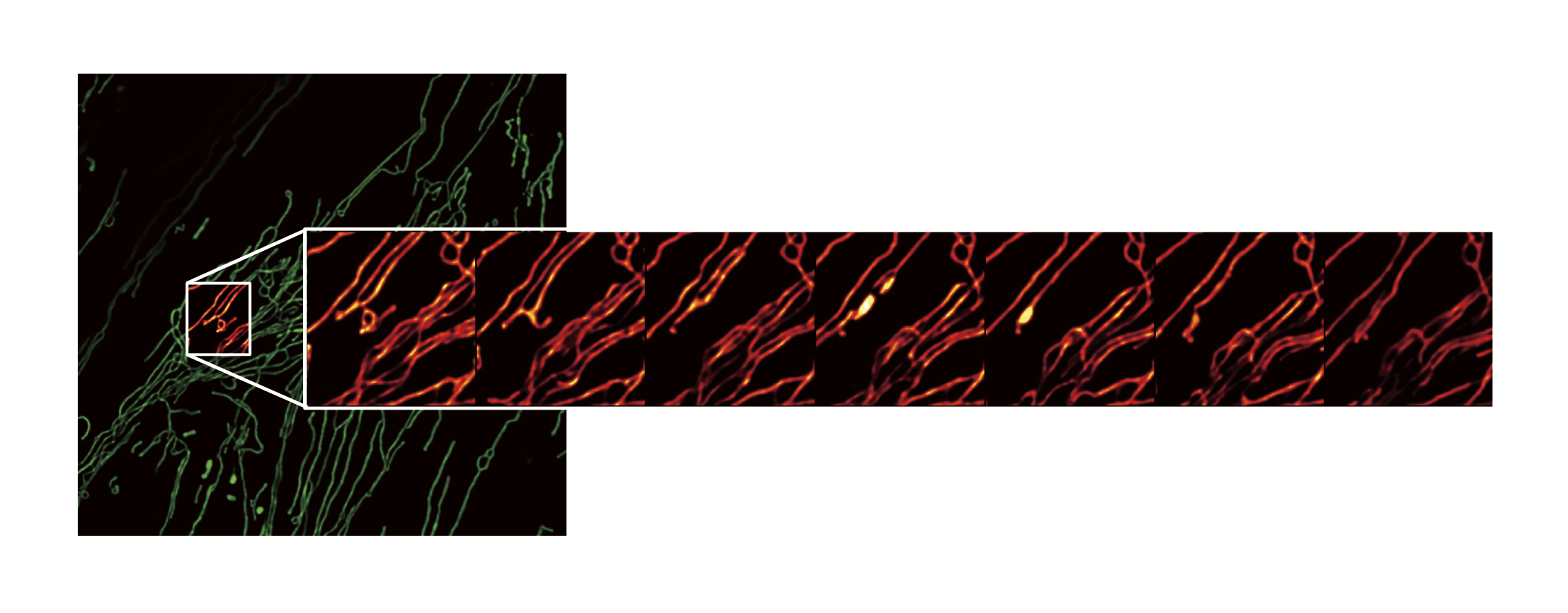
One area of the large field of view (left) is enlarged to show every 10th frame of a fast acquisition timelapse image (right)
The information is current as of the date of publication. It is subject to change without notice.