mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) are one of the stem cells that exist in adults and have the ability to differentiate into mesodermal-derived tissues such as bone, cartilage, blood vessels, and cardiomyocytes. In recent years, it has been reported that they can differentiate into ectoderm-derived neurons and glial cells (which have such functions as supporting neurons) and endoderm-derived hepatocytes.
The International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) has proposed that the common minimum requirements for definition as human MSCs are as follows: (1) plastic-adherent when maintained in standard culture conditions, (2) Must express CD73, CD90, CD105 and lack expression of CD11b or CD14, CD19 or CD79α, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR surface molecules, (3) Must differentiate to osteoblasts, chondrocytes and adipocytes.
MSCs used for clinical purposes are obtained from various tissues such as bone marrow, umbilical cord, cord blood (umbilical cord blood) and fat, and are reported to have important biological activities for tissue repair such as anti-inflammatory effects, secretion of growth factors, and promotion of angiogenesis. It is also said to have low risk of tumor formation. There are already various regenerative medical products in the world.
Reference
Cytotherapy 2006; 8: 315–317.


 Learn how MSCs are used together with its history
Learn how MSCs are used together with its history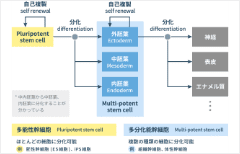 Learn more about MSC characteristics
Learn more about MSC characteristics