stem cells
Stem cells refer to cells that have "self-renewal ability" which enables them to to divide while maintaining "pluripotency" or “multipotency” which enables them to differentiate into other types of cells. They are used not only in basic research, where they are induced to differentiate into specific cells for study, but also in drug discovery screening to look for drug candidates, and in regenerative medicine where the cells themselves are transplanted or administered to patients as drugs.
Stem cells can be roughly divided into three different types. The first are stem cells with totipotency that can differentiate into any cell type, such as fertilized eggs. The second type are stem cells with pluripotency that can differentiate into almost all cells, such as iPS cells (induced pluripotent stem cells/iPSCs) and ES cells (embryonic stem cells/ESCs). Third type are the stem cells that have multipotency, which exist in adults and can differentiate into a limited but plural number of cells, which are called somatic stem cells.


 Learn how stem cells are used together with its history
Learn how stem cells are used together with its history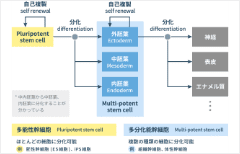 Learn about classification of stem cells and their characteristics
Learn about classification of stem cells and their characteristics