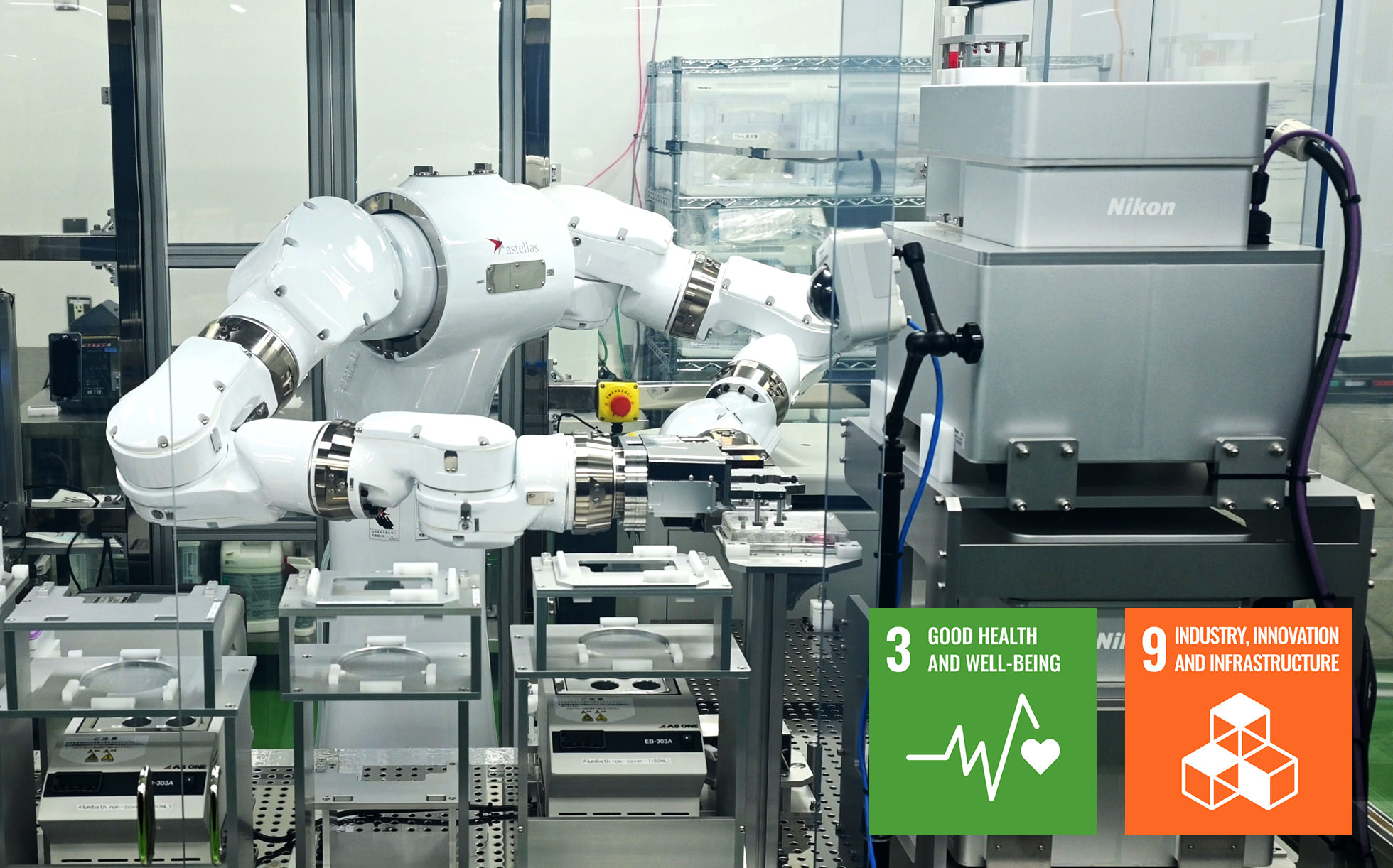
Many of us spend a prolonged amount of time staring at our smartphone and computer screens each day, causing eyestrain. Some people may even notice unusual visual abnormalities such as experiencing blurred vision or seeing distorted shapes. For older individuals, this may be a sign of an eye condition known as “Age-related Macular Degeneration” (AMD). Even for younger people, consistently overworking the eyes can increase the risk of developing this condition in the future. Astellas Pharma Inc. is committed to seeking new treatment alternatives to preserve and restore vision for an ever-growing number of patients. The company is taking on the challenge of automating the manufacture of effective eye cells for AMD treatment, and Nikon’s microscopes are playing a significant role in driving this research and development.
Pursuing cellular-based treatments for ophthalmic disorders
Based on Astellas Pharma Inc.’s company vision “On the forefront of healthcare change to turn innovative science into VALUE for patients”, the company is taking initiatives in pharmaceutical research and development related to various diseases. In particular, the company is prioritizing research and development investments in "Blindness & Regeneration" and actively pursuing research and development of innovative treatment methods. Dr. Hideto Yamaguchi, who heads Chemical & Biological Technology Labs., elaborates, “We’re currently at the clinical trial stage of a project that involves guiding pluripotent stem cells* to differentiate into retinal pigment epithelial cells, a specific type of eye cell, for the treatment of AMD.” The macula, located at the center of the retina, is a crucial area for clear vision and accurate color perception. AMD develops as the retinal pigment epithelial cells become damaged with age, and the macula is affected, leading to symptoms like distorted vision and darkened central vision. In the past, it was thought that damaged retinal pigment epithelial cells couldn’t be regenerated, and so far there hasn’t been a reliable treatment method.

Senior Vice President
CMC Development
Head of Chemical & Biological Technology Labs and Site Head of Tsukuba Bio Research Center
Astellas Pharma Inc.
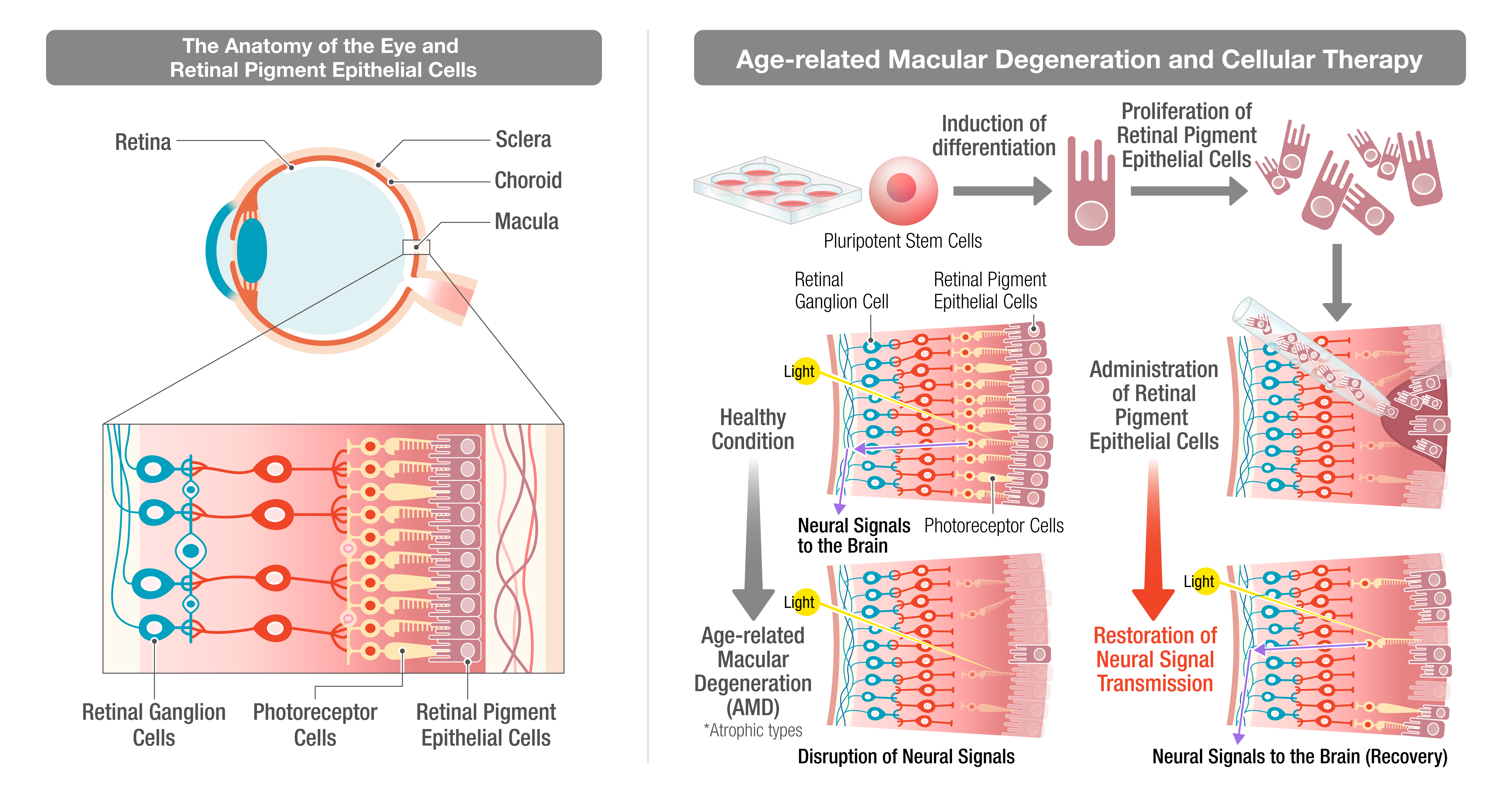
“Our therapeutic approach involves directly introducing (replenishing) differentiated cells from pluripotent stem cells into the affected area. This approach shows potential as a fundamental solution for AMD. Culturing cells from the patient’s own cells (autologous cells) demands time and costs. We are working to automatically generate a large quantity of differentiated cells derived from sources other than their own (allogeneic cells), and supply more patients at a lower cost.” Manufacturing operations such as cell culture, observation and process progress control have been dependent on operators. The Automation Development Team is aiming for consistent and high-volume manufacture and supply of high-quality cells by using the combination of robotic automation and microscopes developed in collaboration with Nikon.
- *Pluripotent stem cells are cells that possess both self-renewal ability through division and the capacity to differentiate into various cell types. Examples include embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells).
Customized microscopes for robotic applications
During our visit to the manufacturing facility for clinical trials at Tsukuba Bio Research Center, we had the opportunity to view operation of the automated cell-culturing system, which is under development. The system is located in a cleanroom area, enclosed with additional shielding. It comprises incubators for cell cultivation, a dual-arm robot (Maholo, manufactured by Robotic Biology Institute Inc.) for various tasks such as plate handling, and the Nikon Advanced Modulation Contrast (NAMC)*1 automated cell observation system, which is a microscope that serves for automated cell observations and assessment, as well as a phase-contrast automated cell observation system. NAMC, which is similar to phase-contrast observation*2, enhances contrast for the observation of cells and proves effective for studying cells differentiated from pluripotent stem cells. The research team members have been using this observation method since the early research stages more than a decade ago. When the Automation Development Team decided to automate the manufacturing process, they reached out to Nikon with the idea of creating a microscope for cell observation that would be robot-operational-friendly. Nikon responded by customizing a microscope product suitable for automated observation of live cells, to meet their specific requirements.
One remarkable aspect of this automated system is the synchronization between the dual-armed robot and the NAMC automated cell observation system. Skillfully utilizing all 15 axes of motion, the robot meticulously handles well plates for cell cultivation. Given the delicate nature of the cells, it’s crucial to minimize any potential impact while ensuring the well plates are kept level during transport. To accommodate these precise movements, the NAMC automated cell observation system features a spacious design for the microscope’s stage, facilitating reception of the well plates from the robot. Once setup is completed, the automated observation process commences. “Cell culture is complex and has long relied on the expertise of skilled operators. Automation via robots can eliminate the challenges of replicating subtle techniques that are difficult to transfer via words or gestures. This can also aid standardization of the culturing process by removing any inconsistencies arising with human operators, ensuring stable, large-scale culture of homogeneous high-quality cells for supply,” explains Dr. Yamaguchi.
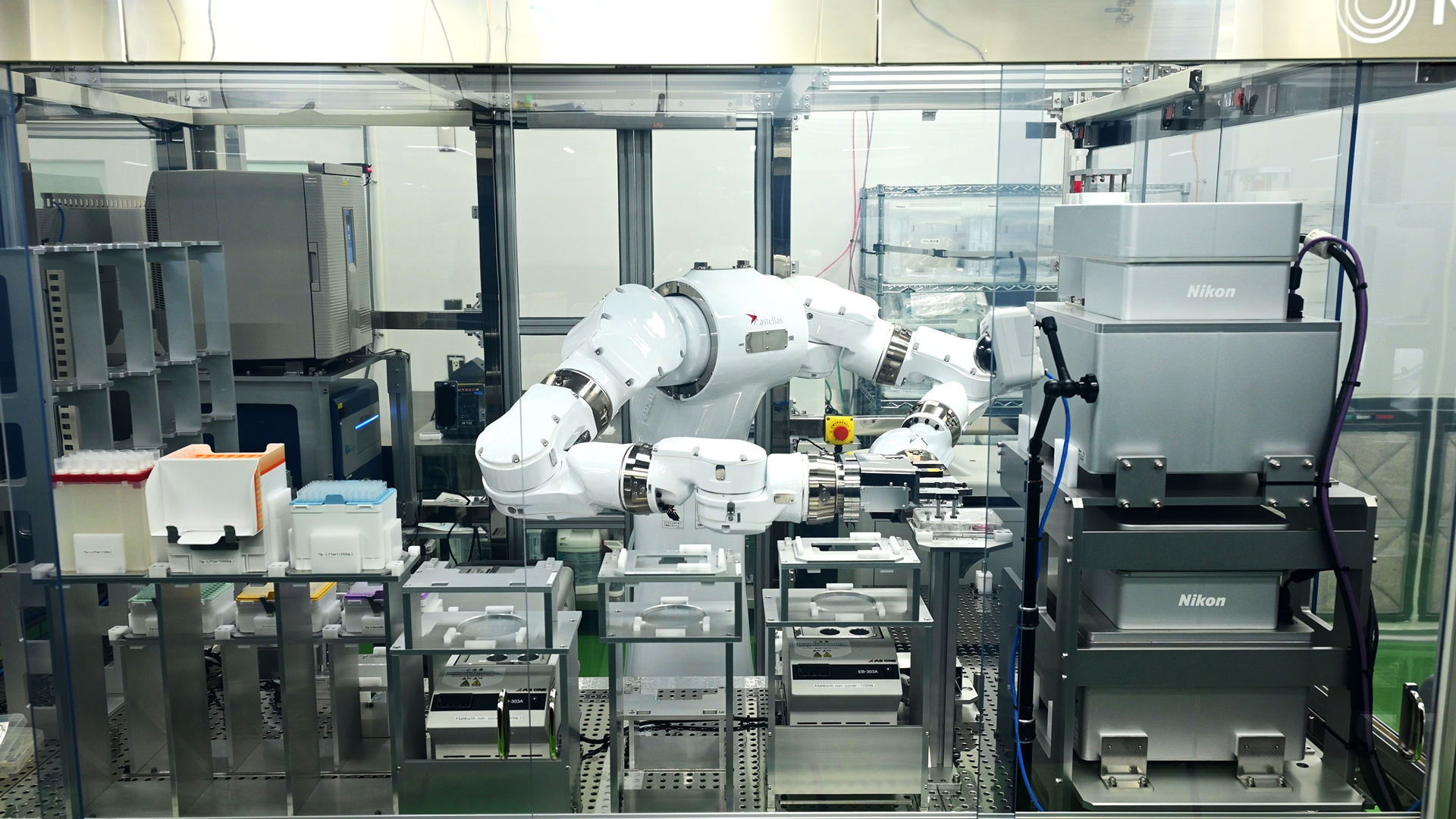

(Upper right: NAMC automated cell observation system, bottom: Phase-contrast automated cell observation system)
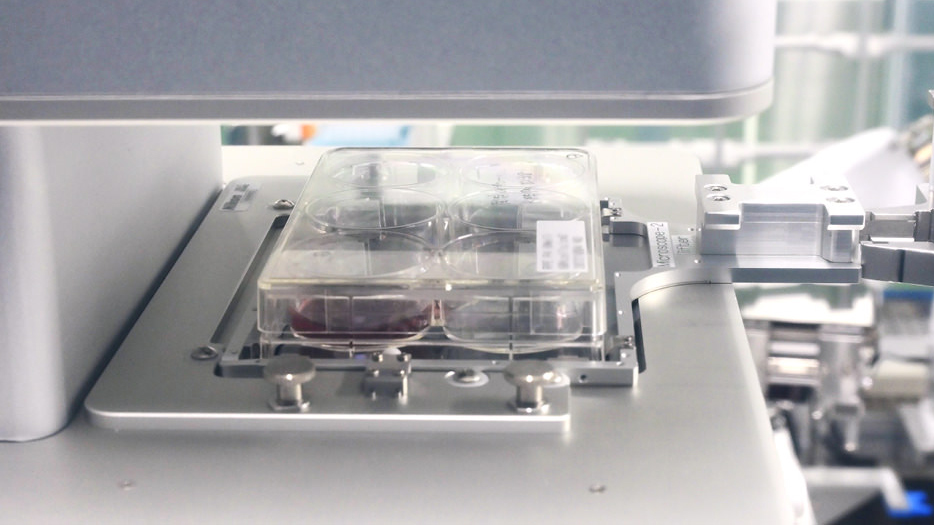
automated cell microscope

In regards to the NAMC automated cell observation system, Dr. Yamaguchi further expresses the development team’s appreciation for its capabilities, “It enables automated observation and assessment just as we had anticipated, while also facilitating the collection of high-quality image data. When integrated with data analysis and AI technology, I imagine it will become capable of playing a pivotal role in driving substantial advancements in future cell culturing. Its exceptional qualities such as waterproofing and chemical resistance also give us confidence in anticipation of its performance in future large-scale cell cultivation lines."
- *1Nikon Advanced Modulation Contrast (NAMC): This is one of the modulation contrast methods that allows the use of plastic well plates, with which differential interference observation cannot usually be performed, and enables the observation of colorless and transparent samples by applying a relief-like contrast.
- *2Phase-contrast observation: An observation method which leverages the diffraction and interference of light to introduce contrast in brightness and darkness when observing colorless and transparent samples.
Ongoing endeavors for next-generation treatments
The use of retinal pigment epithelial cells in treating AMD is anticipated to become a new option for many patients in the coming years. Currently, Astellas Pharma Inc. is actively progressing with cell therapy research and development across various fields, extending beyond ophthalmology to include areas like Immuno-Oncology and Immune Homeostasis. "Microscopic images hold significant information in the area of cell research, and I believe that accumulating more of these data in the future will play a key role in ensuring a stable supply of diverse cell types. I hope to quantitatively assess cell conditions from microscopic image data, as well as to integrate feedback into development and cultivating, in order to boost efforts toward constructing new schemes leveraging AI and IoT technologies," concluded Dr. Yamaguchi, sharing his vision for the future.
As Astellas Pharma Inc. continues to take on challenges toward developing next-generation treatments to enhance the well-being of people everywhere, so will Nikon's microscope technology continue to make valuable contributions to these worthy endeavors.


